Product Description
EMT Pipe Set Screw Coupling
1. American Standard: UL Standard 514B
2. Material: Zine Die Cast
3. Size: 1/2″ to 4″
4. OEM Service
5. Application: Used to bond electrical metallic tubing
| Type: | Die Cast |
|---|---|
| Technique: | Casting |
| Material: | Zinc |
| Usage: | Construction & Decoration, Electrical |
| Section Shape: | Round |
| Size: | From 1/2" to 4" |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What Is a Coupling?
A coupling is a device used to connect two shafts. It transmits power between them and allows for some misalignment or end movement. There are several types of couplings. The most common ones are gear couplings and planetary couplings. However, there are many others as well.
Transfer of energy
Energy coupling is a process by which two biological reactions are linked by sharing energy. The energy released during one reaction can be used to drive the second. It is a very useful mechanism that synchronizes two biological systems. All cells have two types of reactions, exergonic and endergonic, and they are connected through energy coupling.
This process is important for a number of reasons. The first is that it allows the exchange of electrons and their energy. In a single molecule, this energy transfer involves the exchange of two electrons of different energy and spin. This exchange occurs because of the overlap interaction of two MOs.
Secondly, it is possible to achieve quadratic coupling. This is a phenomenon that occurs in circular membrane resonators when the system is statically deflected. This phenomenon has been gaining a great deal of interest as a mechanism for stronger coupling. If this mechanism is employed in a physical system, energy can be transferred on a nanometer scale.
The magnetic field is another important factor that affects the exchange of energy between semiconductor QWs. A strong magnetic field controls the strength of the coupling and the energy order of the exciton. The magnetic field can also influence the direction of polariton-mediated energy transfer. This mechanism is very promising for controlling the routing of excitation in a semiconductor.
Functions
Couplings play a variety of functions, including transferring power, compensating for misalignment, and absorbing shock. These functions depend on the type of shaft being coupled. There are four basic types: angular, parallel, and symmetrical. In many cases, coupling is necessary to accommodate misalignment.
Couplings are mechanical devices that join two rotating pieces of equipment. They are used to transfer power and allow for a small degree of end-to-end misalignment. This allows them to be used in many different applications, such as the transmission from the gearbox to the differential in an automobile. In addition, couplings can be used to transfer power to spindles.
Types
There are two main types of couplings: rigid and flexible. Rigid couplings are designed to prevent relative motion between the two shafts and are suitable for applications where precise alignment is required. However, high stresses in the case of significant misalignment can cause early failure of the coupling. Flexible couplings, on the other hand, allow for misalignment and allow for torque transmission.
A software application may exhibit different types of coupling. The first type involves the use of data. This means that one module may use data from another module for its operation. A good example of data coupling is the inheritance of an object. In a software application, one module can use another module’s data and parameters.
Another type of coupling is a rigid sleeve coupling. This type of coupling has a pipe with a bore that is finished to a specified tolerance. The pipe contains two threaded holes for transmitting torque. The sleeve is secured by a gib head key. This type of coupling may be used in applications where a couple of shafts are close together.
Other types of coupling include common and external. Common coupling occurs when two modules share global data and communication protocols. This type of coupling can lead to uncontrollable error propagation and unforeseen side effects when changes are made to the system. External coupling, on the other hand, involves two modules sharing an external device interface or communication protocol. Both types of coupling involve a shared code structure and depend on the external modules or hardware.
Mechanical couplings are essential in power transmission. They connect rotating shafts and can either be rigid or flexible, depending on the accuracy required. These couplings are used in pumps, compressors, motors, and generators to transmit power and torque. In addition to transferring power, couplings can also prevent torque overload.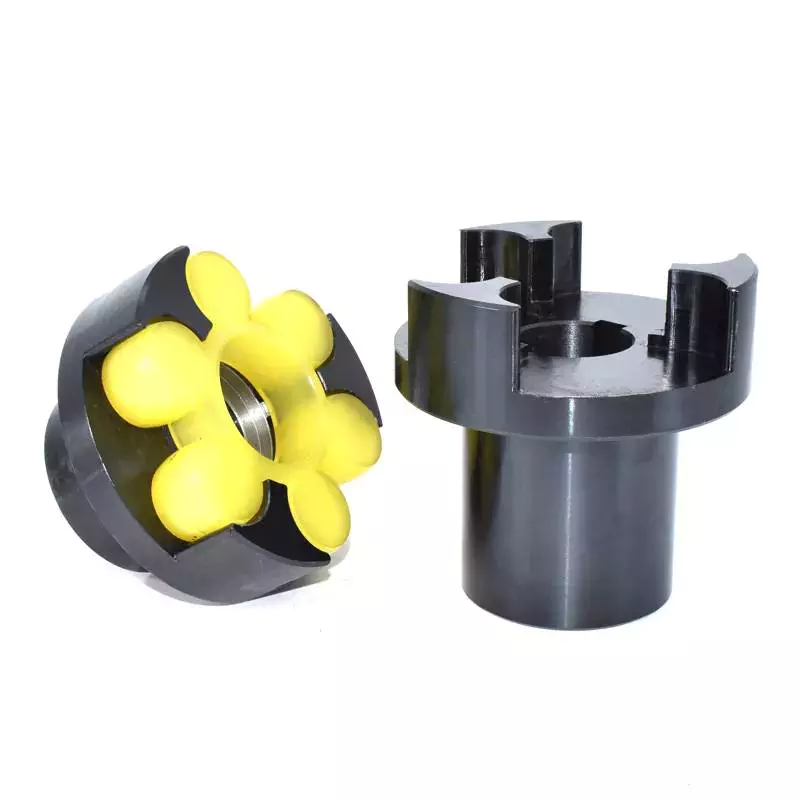
Applications
Different coupling styles are ideal for different applications, and they have different characteristics that influence the coupling’s reliability during operation. These characteristics include stiffness, misalignment capability, ease of installation and maintenance, inherent balance, and speed capability. Selecting the right coupling style for a particular application is essential to minimize performance problems and maximize utility.
It is important to know the requirements for the coupling you choose before you start shopping. A proper selection process takes into account several design criteria, including torque and rpm, acoustic signals, and environmental factors. Once you’ve identified these parameters, you can select the best coupling for the job.
A gear coupling provides a mechanical connection between two rotating shafts. These couplings use gear mesh to transmit torque and power between two shafts. They’re typically used on large industrial machines, but they can also be used in smaller motion control systems. In smaller systems, a zero-backlash coupling design is ideal.
Another type of coupling is the flange coupling. These are easy to manufacture. Their design is similar to a sleeve coupling. But unlike a sleeve coupling, a flange coupling features a keyway on one side and two threaded holes on the other. These couplings are used in medium-duty industrial applications.
Besides being useful for power transmission, couplings can also prevent machine vibration. If vibration occurs in a machine, it can cause it to deviate from its predetermined position, or damage the motor. Couplings, however, help prevent this by absorbing the vibration and shock and preventing damage to expensive parts.
Couplings are heavily used in the industrial machinery and electrical industries. They provide the necessary rotation mechanism required by machinery and other equipment. Coupling suppliers can help customers find the right coupling for a specific application.
Criteria for selecting a coupling
When selecting a coupling for a specific application, there are a number of different factors to consider. These factors vary greatly, as do operating conditions, so selecting the best coupling for your system can be challenging. Some of these factors include horsepower, torque, and speed. You also need to consider the size of the shafts and the geometry of the equipment. Space restrictions and maintenance and installation requirements should also be taken into account. Other considerations can be specific to your system, such as the need for reversing.
First, determine what size coupling you need. The coupling’s size should be able to handle the torque required by the application. In addition, determine the interface connection, such as straight or tapered keyed shafts. Some couplings also feature integral flange connections.
During the specification process, be sure to specify which materials the coupling will be made of. This is important because the material will dictate most of its performance characteristics. Most couplings are made of stainless steel or aluminum, but you can also find ones made of Delrin, titanium, or other engineering-grade materials.
One of the most important factors to consider when selecting a coupling is its torque capability. If the torque rating is not adequate, the coupling can be damaged or break easily. Torque is a major factor in coupling selection, but it is often underestimated. In order to ensure maximum coupling performance, you should also take into consideration the size of the shafts and hubs.
In some cases, a coupling will need lubrication throughout its lifecycle. It may need to be lubricated every six months or even once a year. But there are couplings available that require no lubrication at all. An RBI flexible coupling by CZPT is one such example. Using a coupling of this kind can immediately cut down your total cost of ownership.

editor by CX 2023-07-11
China EMT Fittings Set Screw Coupling UL List coupling distance
Merchandise Description
EMT Established Screw Coupling Zinc
Standard particulars:
| Substance: | Zinc |
| End: | Galvanized |
| Color: |
Silver |
| Variety: | Set Screw / Comperssion |
|
Use: |
For use to bouple 2 finishes of EMT |
| Model Identify: |
TOPELE |
| UL Certificate: | UL No.E506415 |
Specifications:
| Item No: | Measurement: | Dim A(Inch) | Dim B(Inch) |
|
SSCP-fifty |
one/2″ |
one.five hundred | .720 |
|
SSCP-75 |
3/4″ |
1.880 | .945 |
|
SSCP-one hundred |
one” |
two.059 | one.181 |
|
SSCP-a hundred twenty five |
one-1/4″ |
two.504 | one.522 |
|
SSCP-a hundred and fifty |
one-1/2″ |
2.883 | 1.753 |
|
SSCP-200 |
2″ |
3.405 | two.220 |
|
SSCP-250 |
two-1/2″ |
four.000 | 2.913 |
|
SSCP-300 |
three” |
four.488 | 3.563 |
|
SSCP-400 |
4″ |
five.236 | four.488 |
TOPELE EMT Set Screw Coupling Zinc are used in dry area to hook up the ends of 2 unthreaded EMT conduits jointly. CZPT EMT zinc set-screw couplings give concrete limited connections when taped. Furthermore, These set-screw couplings get rid of the need to thread bald conduits to match outdated threaded couplings. EMT conduit couplings are pure zinc material for superb corrosion security in moist place.
FAQ
Q1: Are you manufacture?
A: Indeed,we have manufacturing unit and warehouse in HangZhou HangZhou metropolis.
Q2: How can I request solution samples?
A: The samples are free of charge but courier charge will be collected. Make sure you send out us samples list and courier account quantity.
Q3: How can I ask for a merchandise catalog?
A: The challenging copies of catalogs are free of charge but courier demand will be gathered.
The PDF catalog we can send to you by electronic mail or WeTransfer.
This autumn: What is your payment terms?
A: thirty% T/T deposit,equilibrium against B/L faxed copy
Irrevocable L/C a hundred% at sight and irrevocable.
Q5: How about the shipping and delivery time?
A: Accord to your purchase checklist and amount,mainly supply in 30days.
Why choose us?
one. We are China Leading provide of Electrical Pipe,Strut Channel and Fittings.
two. CZPT is popular model and currently accredited by project engineer in distinct place.
3. Inspected by the Inspection Institution of UL Certification.
4. 100% QC inspection prior to Shipment.
5. Ideal High quality & Ideal Services with Competitive value.
|
US $0.07-2.5 / Piece | |
1,000 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Color: | Silver |
|---|---|
| IP Rating: | IP68 |
| Surface Treatment: | Galvanised |
| Application: | Bouple Two Ends of EMT |
| Material: | Zinc |
| Certification: | UL No.E506415 |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Material: | Zinc |
| Finish: | Galvanized |
| Color: |
Silver |
| Type: | Set Screw / Comperssion |
|
Usage: |
For use to bouple two ends of EMT |
| Brand Name: |
TOPELE |
| UL Certificate: | UL No.E506415 |
###
| Item No: | Size: | Dim A(Inch) | Dim B(Inch) |
|
SSCP-50 |
1/2" |
1.500 | 0.720 |
|
SSCP-75 |
3/4" |
1.880 | 0.945 |
|
SSCP-100 |
1" |
2.059 | 1.181 |
|
SSCP-125 |
1-1/4" |
2.504 | 1.522 |
|
SSCP-150 |
1-1/2" |
2.883 | 1.753 |
|
SSCP-200 |
2" |
3.405 | 2.220 |
|
SSCP-250 |
2-1/2" |
4.000 | 2.913 |
|
SSCP-300 |
3" |
4.488 | 3.563 |
|
SSCP-400 |
4" |
5.236 | 4.488 |
|
US $0.07-2.5 / Piece | |
1,000 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Color: | Silver |
|---|---|
| IP Rating: | IP68 |
| Surface Treatment: | Galvanised |
| Application: | Bouple Two Ends of EMT |
| Material: | Zinc |
| Certification: | UL No.E506415 |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Material: | Zinc |
| Finish: | Galvanized |
| Color: |
Silver |
| Type: | Set Screw / Comperssion |
|
Usage: |
For use to bouple two ends of EMT |
| Brand Name: |
TOPELE |
| UL Certificate: | UL No.E506415 |
###
| Item No: | Size: | Dim A(Inch) | Dim B(Inch) |
|
SSCP-50 |
1/2" |
1.500 | 0.720 |
|
SSCP-75 |
3/4" |
1.880 | 0.945 |
|
SSCP-100 |
1" |
2.059 | 1.181 |
|
SSCP-125 |
1-1/4" |
2.504 | 1.522 |
|
SSCP-150 |
1-1/2" |
2.883 | 1.753 |
|
SSCP-200 |
2" |
3.405 | 2.220 |
|
SSCP-250 |
2-1/2" |
4.000 | 2.913 |
|
SSCP-300 |
3" |
4.488 | 3.563 |
|
SSCP-400 |
4" |
5.236 | 4.488 |
Programming With Couplings
A coupling is a mechanical device that connects two shafts together and transmits power. Its purpose is to join rotating equipment and allows some degree of end-movement or misalignment. There are many different types of couplings. It’s important to choose the right one for your application.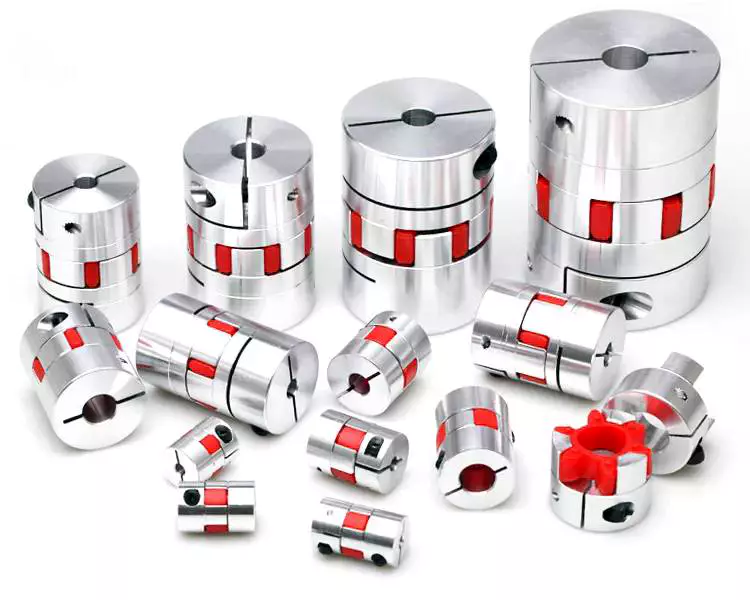
Mechanical connection between two shafts
There are many ways to achieve mechanical connection between two shafts, including the use of a coupling. One common type is the beam coupling, which is also known as a helical coupling. It is used for transmission of torque between two shafts. This type of connection accommodates axial, parallel and angular misalignments.
The hubs and shafts of a worm gear are connected together by a coupling. This mechanical connection allows one shaft to turn another without causing a mechanical failure. This type of coupling is made from sliding or rubbing parts to transfer torque. However, the coupling is not designed to withstand jerks, so it isn’t suitable for high-speed applications.
The use of a coupling is common in machinery and equipment. It helps transmit power from one drive shaft to the other, while adding mechanical flexibility. It is also useful for reducing the impact and vibration caused by misalignment. It also protects the drive shaft components from wear and tear.
A double-hook coupling can be used to provide a uniform angular velocity at the driven shaft. Another example is a double-jointed coupling. A double-jointed coupling can be used to connect shafts that are not directly intersecting. The double-jointed yoke can be used for the same purpose.
A shaft coupling is a device that maintains a strong mechanical connection between two shafts. It transfers motion from one shaft to another, at all loads and misalignments. Unlike a conventional linkage, a shaft coupling isn’t designed to allow relative motion between the two shafts. Couplings often serve several purposes in a machine, but their primary use is torque and power transmission.
Functions that control the flow of another function
One of the simplest programming constructs is a function that controls the flow of another function. A function can take an argument and return a different value, but it must be ready to return before it can pass that value to another function. To do this, you can use the goto statement and the if statement. Another way to control flow is to use a conditional statement.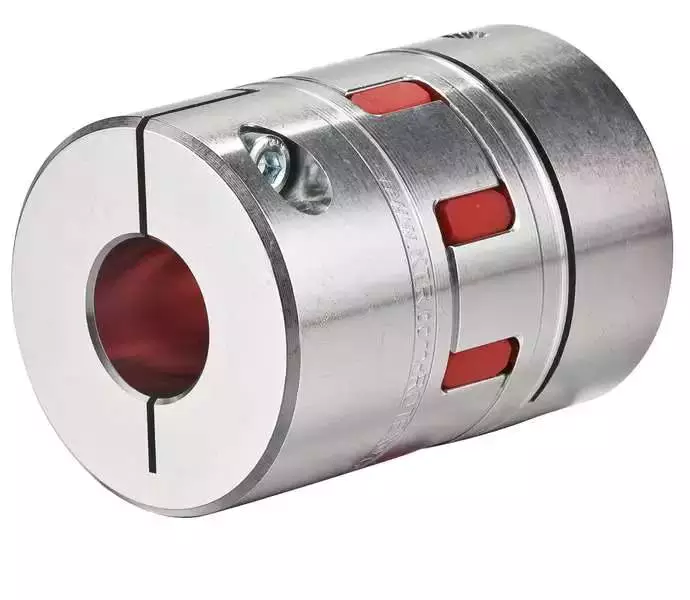
Criteria for selecting a coupling
There are several important factors to consider when choosing the right coupling. One of the most important factors is coupling stiffness, which depends on the material used and the shape. The stiffness of a coupling determines its ability to resist elastic deformation. A stiff coupling is desirable for certain types of applications, but it’s undesirable for others. Stiffness can reduce the performance of a system if there’s too much inertia. To avoid this, ensure that the coupling you choose is within the recommended limits.
The size of a coupling is also important. Different coupling types can accommodate different shaft sizes and shapes. Some couplings have special features, such as braking and shear pin protection. When choosing a coupling, you should also consider the type of driven equipment. If you need to connect a high-torque motor, for example, you’ll want to choose a gear coupling. Likewise, a high-speed machine may require a disc coupling.
Another factor to consider when selecting a coupling is the torque rating. Despite its importance, it’s often underestimated. The torque rating is defined as the torque of the coupling divided by its OD. In some cases, torque may fluctuate during a cycle, requiring a coupling with a higher torque rating.
Torsionally flexible couplings are also important to consider. Their design should be able to withstand the torque required during operation, as well as the required speed. The coupling should also have a high degree of torsional stiffness, as well as damping. Furthermore, a damping coupling can reduce the energy wasted through vibration.
The sizing of a coupling is also determined by the torque. Many engineers use torque to select the correct coupling size, but they also take into consideration torsional flexibility and torsional stiffness. For example, a shaft may be able to handle large torque without damaging the coupling, while a disk may be unable to handle large amounts of torque.
Besides torque, another important consideration in coupling selection is the cost. While a coupling may be cheaper, it may be less reliable or easier to maintain. Couplings that are difficult to service may not last as long. They may also require frequent maintenance. If that’s the case, consider purchasing a coupling with a low service factor.
There are many different types of couplings. Some require additional lubrication throughout their lifetime, while others are 100% lubrication-free. An example of a 100% lubrication-free coupling is the RBI flexible coupling from CZPT. This type of coupling can significantly reduce your total cost of ownership.
In addition to the above-mentioned benefits, elastomeric couplings are low-cost and need little maintenance. While they are often cheaper than metallic couplings, they also have excellent shock absorption and vibration dampening properties. However, they are susceptible to high temperatures. Also, they are difficult to balance as an assembly, and have limited overload torque capacity.

editor by czh 2022-12-29