Merchandise Description
HDPE Fitting Plumbing Fitting Pn sixteen PP Compression Fitting Woman Threaded Coupling
Product Description
IRRIPLAST PP compression fittings line has been made for the conveyance of fluids at large pressures, for water conveyance, for potable water distribution and apps in the thermo-hydraulic sector. This product line is accordance with the most significant intercontinental standards in phrases of mechanical homes and alimentary compatibilities.
Technical information
| Portion | Material |
| Human body(A) | Polypropylene co-polymer(PP-B) of outstanding mechanical houses even at high temperature. |
| Blocking bush(D) | Polypropylene |
| Nut(B) | Polypropylene with dye learn of substantial steadiness to UV rays andsolidity to heat( S grade according to common DIN54004) |
| Clinching ring(C) | Polyacetal resin(POM)with higher mechanical resistance And hardness |
| O Ring gasket(E) | Specific elastomeric acrylonitrile rubber(EPDM) for alimentary use |
| Reinforcing ring | AISI 430 (UNI X8Cr17,W,nr 14828)Stainless metal for woman threads from 1″to 4″ |
| PN sixteen sort | Code | Size | Weight (g/laptop) | PCS/BAG | PCS/CTN |
| Female thread adaptor | 1003 | 20*1/2 | forty four | 30 | 420 |
| 20*3/four | forty five | twenty | 400 | ||
| 20*1 | 51 | twenty | 360 | ||
| twenty five*1/two | sixty four | 20 | 240 | ||
| 25*3/four | sixty five | 20 | 240 | ||
| twenty five*1 | 76 | twenty | 220 | ||
| 32*1/2 | 94 | ten | one hundred sixty | ||
| 32*3/four | ninety six | ten | a hundred and sixty | ||
| 32*1 | a hundred | ten | 160 | ||
| 32* 1 1/four | 58 | ten | a hundred and sixty | ||
| forty*1 | 172 | 6 | ninety six | ||
| 40*eleven/4 | 172 | 6 | ninety | ||
| 40*11/two | 184 | 6 | 90 | ||
| fifty*11/4 | 279 | sixty | |||
| fifty*11/2″ | 286 | 60 | |||
| fifty*2 | 295 | fifty two | |||
| 63*11/4 | 465 | 30 | |||
| sixty three*11/two | 484 | 28 | |||
| sixty three*2 | 502 | 28 | |||
| 75*two | 574 | 27 | |||
| seventy five*2 1/two | 588 | 24 | |||
| 75*three | 653 | 24 | |||
| 90*2 1/two | 803 | thirteen | |||
| ninety*three | 858 | thirteen | |||
| 90*4″ | 931 | 13 | |||
| a hundred and ten*three | 1372 | eight | |||
| 110*4 | 1382 | eight |
Operating PRESSURES
IRRIPLAST PP compression fittings allows the optimum working strain(PN~PFA*) of 16 bar(UNI 9562) for diameters from 16mm to 63mm and PN10 bar for diameters from 75mm to 110mm, at the temperature of 20°C.Greatest allowable doing work pressures connected to the length of stress and temperature.
Features
one. Light weight, effortless to load and unload
2. Great chemicals and medication resistance
3. Modest resistance to fluidity
4. Robust mechanical power
5. Good electrical insulation
6. Drinking water high quality unaffected
seven. Basic installation
Application
one. Composition Engineering
two. Water source program
3. for Agriculture Irrigation
Reference Specifications
Proportions: UNI 9561
Operating Strain: UNI 9562,DIN 8076-3,ISO 14236,BRL-K03.
Polyethylene(PE)pipes: UNI 7990,DIN 8074,UNI EN 12201
Threads: UNI ISO7/1,UNI EN 10026-1,ANSI ASME B1-twenty.one
Flanges: DIN 2501-1,UNI EN 1452-3.IS 7005-two
Principal Products
See a lot more goods,you can simply click goods search phrases…
| PPR Pipe | PPR Fitting |
| PP Union Ball Valve | PP Compression Fitting |
| Clamp Saddle | Solenoid Valve |
Sprinkler |
PVC Ball Valves |
Company Profile
OTHER Element Services FOR YOU
1.Any inquiries will be replied inside of 24 hrs.
2.Specialist producer.
three.OEM is available.
4.High good quality, regular types,sensible&competitive price,rapidly direct time.
five.Faster shipping: Sample will be ready in 2-3 days.
six.Shipping and delivery: We have strong cooperation with DHL,TNT,UPS,MSK,China Delivery,etc.
FAQ
1.What is your MOQ?
Our MOQ is generally 5 CTNS for measurement from 20-50mm.
two.What is your delievery time?
The time of delievery is all around thirty-45days.
3.What is your payment terms?
We take 30% T/T in advance,70% before cargo .or 100% L/C.
four.What is the shipping and delivery port?
We ship the goods to HangZhou or ZheJiang port.
five.What is the deal with of your company?
Our company is situated in the HangZhou, HangZhou ZHangZhoug Province,China.You are welcomed to visit our manufacturing unit.
six.How about the samples?
we could send out you the samples for free of charge, and you need to have to pay out the courier payment.
If there are way too a lot samples, then you also want to undertake the sample fee.
| Connection: | Female |
|---|---|
| Head Code: | Round |
| Thread Distribution: | Internal Thread |
| Surface: | Polish |
| Material: | Plastic |
| Technics: | Casting |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 3/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Part | Material |
| Body(A) | Polypropylene co-polymer(PP-B) of exceptional mechanical properties even at high temperature. |
| Blocking bush(D) | Polypropylene |
| Nut(B) | Polypropylene with dye master of high stability to UV rays andsolidity to heat( S grade according to standard DIN54004) |
| Clinching ring(C) | Polyacetal resin(POM)with high mechanical resistance And hardness |
| O Ring gasket(E) | Special elastomeric acrylonitrile rubber(EPDM) for alimentary use |
| Reinforcing ring | AISI 430 (UNI X8Cr17,W,nr 14828)Stainless steel for female threads from 1"to 4" |
###
| PN 16 type | Code | Size | Weight (g/pc) | PCS/BAG | PCS/CTN |
| Female thread adaptor | 1003 | 20*1/2 | 44 | 30 | 420 |
| 20*3/4 | 45 | 20 | 400 | ||
| 20*1 | 51 | 20 | 360 | ||
| 25*1/2 | 64 | 20 | 240 | ||
| 25*3/4 | 65 | 20 | 240 | ||
| 25*1 | 76 | 20 | 220 | ||
| 32*1/2 | 94 | 10 | 160 | ||
| 32*3/4 | 96 | 10 | 160 | ||
| 32*1 | 100 | 10 | 160 | ||
| 32* 1 1/4 | 58 | 10 | 160 | ||
| 40*1 | 172 | 6 | 96 | ||
| 40*11/4 | 172 | 6 | 90 | ||
| 40*11/2 | 184 | 6 | 90 | ||
| 50*11/4 | 279 | 0 | 60 | ||
| 50*11/2" | 286 | 0 | 60 | ||
| 50*2 | 295 | 0 | 52 | ||
| 63*11/4 | 465 | 0 | 30 | ||
| 63*11/2 | 484 | 0 | 28 | ||
| 63*2 | 502 | 0 | 28 | ||
| 75*2 | 574 | 0 | 27 | ||
| 75*2 1/2 | 588 | 0 | 24 | ||
| 75*3 | 653 | 0 | 24 | ||
| 90*2 1/2 | 803 | 0 | 13 | ||
| 90*3 | 858 | 0 | 13 | ||
| 90*4" | 931 | 0 | 13 | ||
| 110*3 | 1372 | 0 | 8 | ||
| 110*4 | 1382 | 0 | 8 |
###
| PPR Pipe | PPR Fitting |
| PP Union Ball Valve | PP Compression Fitting |
| Clamp Saddle | Solenoid Valve |
Sprinkler |
PVC Ball Valves |
| Connection: | Female |
|---|---|
| Head Code: | Round |
| Thread Distribution: | Internal Thread |
| Surface: | Polish |
| Material: | Plastic |
| Technics: | Casting |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 3/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Part | Material |
| Body(A) | Polypropylene co-polymer(PP-B) of exceptional mechanical properties even at high temperature. |
| Blocking bush(D) | Polypropylene |
| Nut(B) | Polypropylene with dye master of high stability to UV rays andsolidity to heat( S grade according to standard DIN54004) |
| Clinching ring(C) | Polyacetal resin(POM)with high mechanical resistance And hardness |
| O Ring gasket(E) | Special elastomeric acrylonitrile rubber(EPDM) for alimentary use |
| Reinforcing ring | AISI 430 (UNI X8Cr17,W,nr 14828)Stainless steel for female threads from 1"to 4" |
###
| PN 16 type | Code | Size | Weight (g/pc) | PCS/BAG | PCS/CTN |
| Female thread adaptor | 1003 | 20*1/2 | 44 | 30 | 420 |
| 20*3/4 | 45 | 20 | 400 | ||
| 20*1 | 51 | 20 | 360 | ||
| 25*1/2 | 64 | 20 | 240 | ||
| 25*3/4 | 65 | 20 | 240 | ||
| 25*1 | 76 | 20 | 220 | ||
| 32*1/2 | 94 | 10 | 160 | ||
| 32*3/4 | 96 | 10 | 160 | ||
| 32*1 | 100 | 10 | 160 | ||
| 32* 1 1/4 | 58 | 10 | 160 | ||
| 40*1 | 172 | 6 | 96 | ||
| 40*11/4 | 172 | 6 | 90 | ||
| 40*11/2 | 184 | 6 | 90 | ||
| 50*11/4 | 279 | 0 | 60 | ||
| 50*11/2" | 286 | 0 | 60 | ||
| 50*2 | 295 | 0 | 52 | ||
| 63*11/4 | 465 | 0 | 30 | ||
| 63*11/2 | 484 | 0 | 28 | ||
| 63*2 | 502 | 0 | 28 | ||
| 75*2 | 574 | 0 | 27 | ||
| 75*2 1/2 | 588 | 0 | 24 | ||
| 75*3 | 653 | 0 | 24 | ||
| 90*2 1/2 | 803 | 0 | 13 | ||
| 90*3 | 858 | 0 | 13 | ||
| 90*4" | 931 | 0 | 13 | ||
| 110*3 | 1372 | 0 | 8 | ||
| 110*4 | 1382 | 0 | 8 |
###
| PPR Pipe | PPR Fitting |
| PP Union Ball Valve | PP Compression Fitting |
| Clamp Saddle | Solenoid Valve |
Sprinkler |
PVC Ball Valves |
What Is a Coupling?
A coupling is a device used to connect two shafts. It transmits power between them and allows for some misalignment or end movement. There are several types of couplings. The most common ones are gear couplings and planetary couplings. However, there are many others as well.
Transfer of energy
Energy coupling is a process by which two biological reactions are linked by sharing energy. The energy released during one reaction can be used to drive the second. It is a very useful mechanism that synchronizes two biological systems. All cells have two types of reactions, exergonic and endergonic, and they are connected through energy coupling.
This process is important for a number of reasons. The first is that it allows the exchange of electrons and their energy. In a single molecule, this energy transfer involves the exchange of two electrons of different energy and spin. This exchange occurs because of the overlap interaction of two MOs.
Secondly, it is possible to achieve quadratic coupling. This is a phenomenon that occurs in circular membrane resonators when the system is statically deflected. This phenomenon has been gaining a great deal of interest as a mechanism for stronger coupling. If this mechanism is employed in a physical system, energy can be transferred on a nanometer scale.
The magnetic field is another important factor that affects the exchange of energy between semiconductor QWs. A strong magnetic field controls the strength of the coupling and the energy order of the exciton. The magnetic field can also influence the direction of polariton-mediated energy transfer. This mechanism is very promising for controlling the routing of excitation in a semiconductor.
Functions
Couplings play a variety of functions, including transferring power, compensating for misalignment, and absorbing shock. These functions depend on the type of shaft being coupled. There are four basic types: angular, parallel, and symmetrical. In many cases, coupling is necessary to accommodate misalignment.
Couplings are mechanical devices that join two rotating pieces of equipment. They are used to transfer power and allow for a small degree of end-to-end misalignment. This allows them to be used in many different applications, such as the transmission from the gearbox to the differential in an automobile. In addition, couplings can be used to transfer power to spindles.
Types
There are two main types of couplings: rigid and flexible. Rigid couplings are designed to prevent relative motion between the two shafts and are suitable for applications where precise alignment is required. However, high stresses in the case of significant misalignment can cause early failure of the coupling. Flexible couplings, on the other hand, allow for misalignment and allow for torque transmission.
A software application may exhibit different types of coupling. The first type involves the use of data. This means that one module may use data from another module for its operation. A good example of data coupling is the inheritance of an object. In a software application, one module can use another module’s data and parameters.
Another type of coupling is a rigid sleeve coupling. This type of coupling has a pipe with a bore that is finished to a specified tolerance. The pipe contains two threaded holes for transmitting torque. The sleeve is secured by a gib head key. This type of coupling may be used in applications where a couple of shafts are close together.
Other types of coupling include common and external. Common coupling occurs when two modules share global data and communication protocols. This type of coupling can lead to uncontrollable error propagation and unforeseen side effects when changes are made to the system. External coupling, on the other hand, involves two modules sharing an external device interface or communication protocol. Both types of coupling involve a shared code structure and depend on the external modules or hardware.
Mechanical couplings are essential in power transmission. They connect rotating shafts and can either be rigid or flexible, depending on the accuracy required. These couplings are used in pumps, compressors, motors, and generators to transmit power and torque. In addition to transferring power, couplings can also prevent torque overload.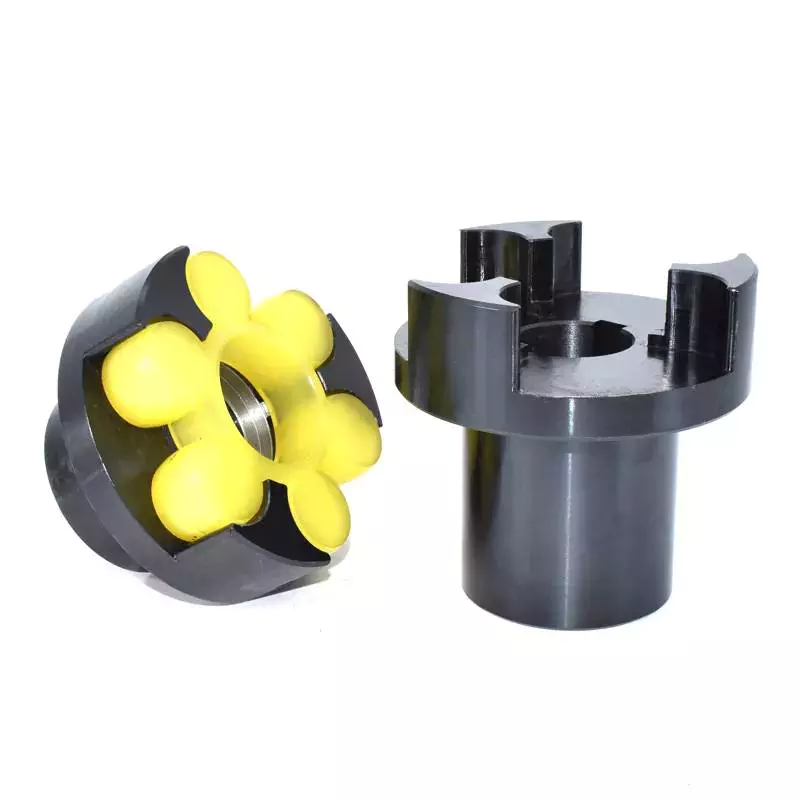
Applications
Different coupling styles are ideal for different applications, and they have different characteristics that influence the coupling’s reliability during operation. These characteristics include stiffness, misalignment capability, ease of installation and maintenance, inherent balance, and speed capability. Selecting the right coupling style for a particular application is essential to minimize performance problems and maximize utility.
It is important to know the requirements for the coupling you choose before you start shopping. A proper selection process takes into account several design criteria, including torque and rpm, acoustic signals, and environmental factors. Once you’ve identified these parameters, you can select the best coupling for the job.
A gear coupling provides a mechanical connection between two rotating shafts. These couplings use gear mesh to transmit torque and power between two shafts. They’re typically used on large industrial machines, but they can also be used in smaller motion control systems. In smaller systems, a zero-backlash coupling design is ideal.
Another type of coupling is the flange coupling. These are easy to manufacture. Their design is similar to a sleeve coupling. But unlike a sleeve coupling, a flange coupling features a keyway on one side and two threaded holes on the other. These couplings are used in medium-duty industrial applications.
Besides being useful for power transmission, couplings can also prevent machine vibration. If vibration occurs in a machine, it can cause it to deviate from its predetermined position, or damage the motor. Couplings, however, help prevent this by absorbing the vibration and shock and preventing damage to expensive parts.
Couplings are heavily used in the industrial machinery and electrical industries. They provide the necessary rotation mechanism required by machinery and other equipment. Coupling suppliers can help customers find the right coupling for a specific application.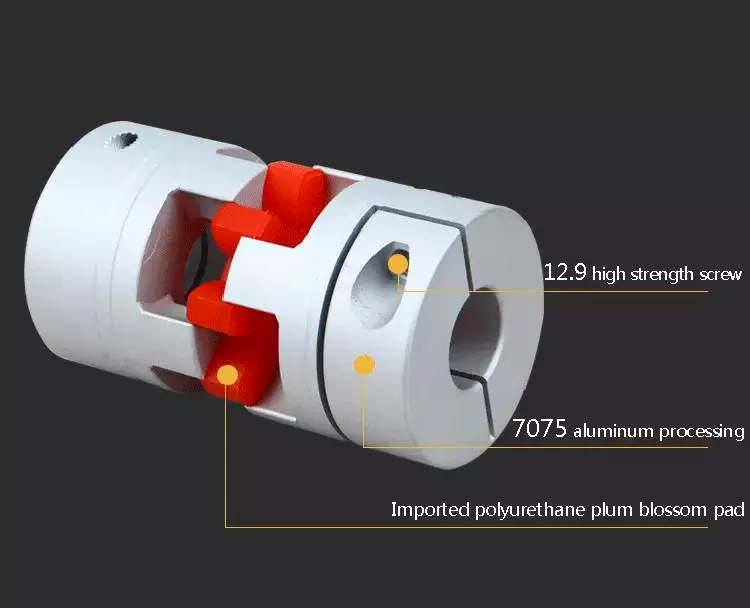
Criteria for selecting a coupling
When selecting a coupling for a specific application, there are a number of different factors to consider. These factors vary greatly, as do operating conditions, so selecting the best coupling for your system can be challenging. Some of these factors include horsepower, torque, and speed. You also need to consider the size of the shafts and the geometry of the equipment. Space restrictions and maintenance and installation requirements should also be taken into account. Other considerations can be specific to your system, such as the need for reversing.
First, determine what size coupling you need. The coupling’s size should be able to handle the torque required by the application. In addition, determine the interface connection, such as straight or tapered keyed shafts. Some couplings also feature integral flange connections.
During the specification process, be sure to specify which materials the coupling will be made of. This is important because the material will dictate most of its performance characteristics. Most couplings are made of stainless steel or aluminum, but you can also find ones made of Delrin, titanium, or other engineering-grade materials.
One of the most important factors to consider when selecting a coupling is its torque capability. If the torque rating is not adequate, the coupling can be damaged or break easily. Torque is a major factor in coupling selection, but it is often underestimated. In order to ensure maximum coupling performance, you should also take into consideration the size of the shafts and hubs.
In some cases, a coupling will need lubrication throughout its lifecycle. It may need to be lubricated every six months or even once a year. But there are couplings available that require no lubrication at all. An RBI flexible coupling by CZPT is one such example. Using a coupling of this kind can immediately cut down your total cost of ownership.

editor by czh 2023-01-09